This is Tonbo Imaging's latest offering. This is what I like about them they keep investing in R&D with or without orders.
This is called VOODOO. This is what they have to say about it :
"VOODOO is based on a shutterless HawkVision thermal imaging core with a 640×480 micro bolometer array on a latest gen 12-micron pitch and advanced thermal image processing.
It is offered with a flip in / out Picatinny mount allowing the gunner to quickly switch between day scope and TI scope in CLIP ON mode. The mount also allows the gunner to quickly detach the sight with a single lever and snap fit it on the helmet with the same mount interface, without the need for any extra tools.
Salient Features :



This is TUVE. It is a compact, lightweight and low power uncooled imaging platform for full frame rate PAL/NTSC QVGA/VGA/XGA thermal sensors enabling outstanding sensitivity and excellent image quality. TUVE supports multiple color palettes and can provide output in raw 14bit digital video, processed 8 bit BT656 video or composite video output format (NTSC/PAL system). Shutterless operation provides a stable, crystal-clear video stream without loss of frames.
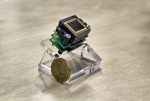

Vision Image Processor (VIP) is a video processor designed for platforms with limited real estate and computational resources. It is capable of ingesting video feeds from analog sources and performs real-time electronic image stabilization and target tracking on HD and SD videos. It is optimized to work in real time with day camera or IR camera video feeds.

They also have airborne gimballed EOTS. Avenger-S is a family of multi axis stabilised electro optical sight for aerial surveillance and reconnaissance. It is designed as a modular but and integrated system with a cooled MWIR thermal imager, short wave infrared imager, color HD imager, low light TV and spotter, IR pointer, IR illuminator, Laser Range Finder and GPS and compass for very long range surveillance, reconnaissance and targeting applications.


This is called VOODOO. This is what they have to say about it :
"VOODOO is based on a shutterless HawkVision thermal imaging core with a 640×480 micro bolometer array on a latest gen 12-micron pitch and advanced thermal image processing.
It is offered with a flip in / out Picatinny mount allowing the gunner to quickly switch between day scope and TI scope in CLIP ON mode. The mount also allows the gunner to quickly detach the sight with a single lever and snap fit it on the helmet with the same mount interface, without the need for any extra tools.
Salient Features :
- Integrated NIR / VIS pointer
- No Re zeroing required
- Aircraft grade aluminum construction
- Easy and Intuitive user interface
- Weapon compatibility upto 0.308 cal semi automatic



This is TUVE. It is a compact, lightweight and low power uncooled imaging platform for full frame rate PAL/NTSC QVGA/VGA/XGA thermal sensors enabling outstanding sensitivity and excellent image quality. TUVE supports multiple color palettes and can provide output in raw 14bit digital video, processed 8 bit BT656 video or composite video output format (NTSC/PAL system). Shutterless operation provides a stable, crystal-clear video stream without loss of frames.


Vision Image Processor (VIP) is a video processor designed for platforms with limited real estate and computational resources. It is capable of ingesting video feeds from analog sources and performs real-time electronic image stabilization and target tracking on HD and SD videos. It is optimized to work in real time with day camera or IR camera video feeds.

They also have airborne gimballed EOTS. Avenger-S is a family of multi axis stabilised electro optical sight for aerial surveillance and reconnaissance. It is designed as a modular but and integrated system with a cooled MWIR thermal imager, short wave infrared imager, color HD imager, low light TV and spotter, IR pointer, IR illuminator, Laser Range Finder and GPS and compass for very long range surveillance, reconnaissance and targeting applications.


























